
Lab 8 - Module 2 - Anatomy of the Anterior and Lateral Compartments: Page 3 of 3
×
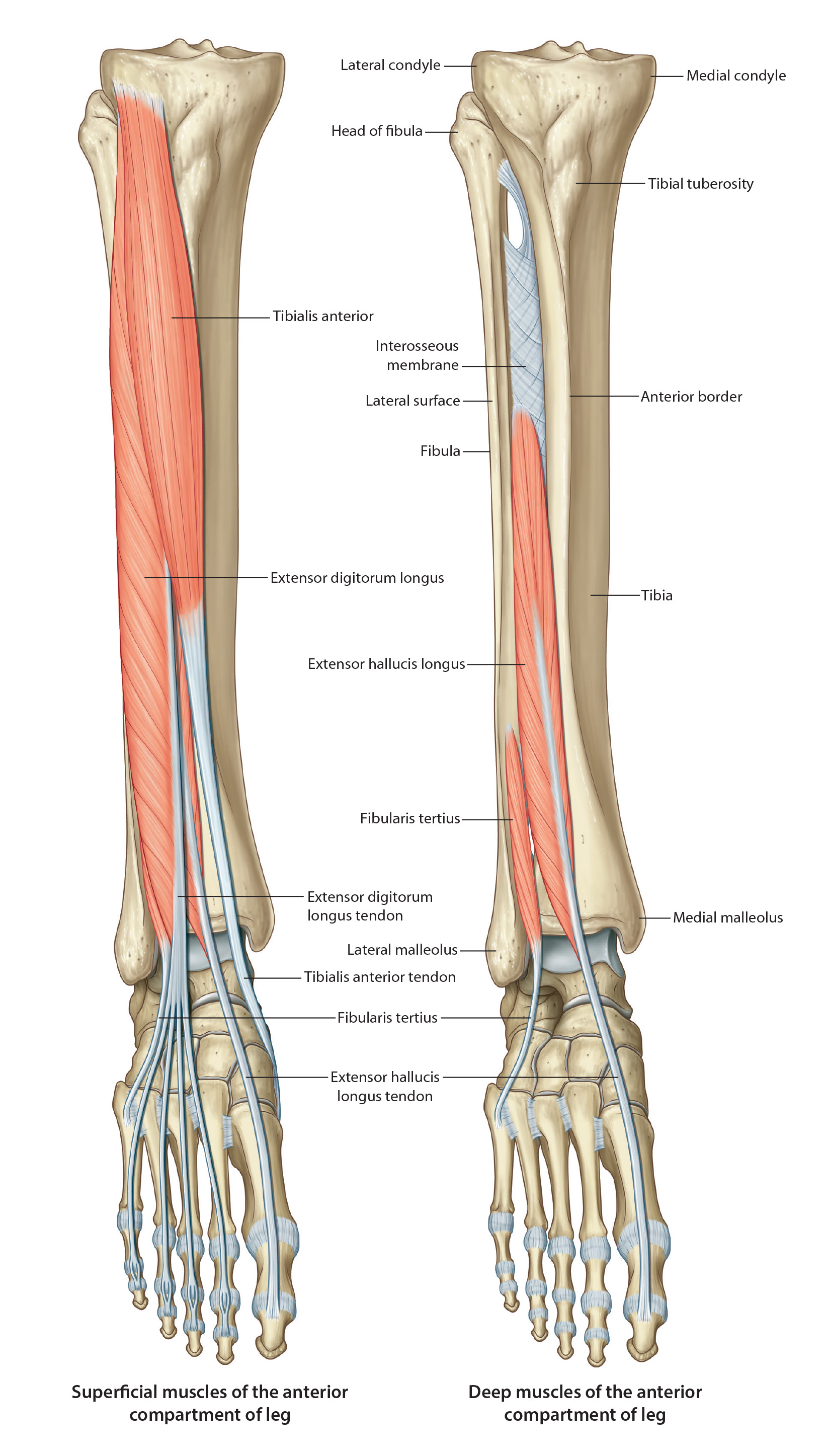
Lateral Compartment of the Leg
 |
| Tap on image to enlarge |
| The lateral compartment is bounded by the lateral surface of the fibula, anterior and posterior crural intermuscular septa, and crural fascia. It contains two muscles, one nerve and receives its blood supply from perforating branches of the fibular artery in the deep posterior compartment. The tendons of the two muscles are held in place by the superior and inferior fibular retinaculum (extensions of the crural fascia). The muscles are everters and plantar flexors of the ankle. |
| The Arterial Supply comes from perforating branches off the fibular artery (a branch off the posterior tibial artery in the posterior compartment). No vessel travels through the lateral compartment. |
| Add the Fibularis (Peroneal) Muscle Group. This group of muscles include the following components: |
| Add the Peroneus (Fibularis) Brevis Muscle. |
|
Origin - Distal 2/3rds of the of the fibula Insertion - Lateral surface of the base of the fifth metatarsal Innervation - Superficial Peroneal (fibular) Nerve Action - Eversion of the foot; weak plantar flexor of ankle |
| Add the Peroneus (Fibularis) Longus Muscle. |
|
Origin - Head of the fibula and the superior 2/3rds of the lateral surface of the fibula Insertion - Lateral aspect of the base of the first metatarsal and the plantar aspect of the medial cuneiform Innervation - Superficial Peroneal (fibular) Nerve Action - Eversion of the foot; weak plantar flexor of ankle |
| Add the Fibularis (peroneus) Tertius. |
|
Origin - Distal 1/3 of the anterior surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane Insertion - Dorsal surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal Innervation - Deep Fibular (peroneal) Nerve Action - Dorsiflexion of the ankle and eversion |