
Thorax Lab 1 Module 1
OBJECTIVES:2.1.1 Compare the anatomical features of typical and atypical ribs. 2.1.2 Identify the osseous components of the sternum. 2.1.3 Identify the joints and ligaments involved in the movements of respiration. 2.1.4 Demonstrate the anatomy, function, and innervation of the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm. 2.1.5 Identify the accessory muscles of respiration and describe their roles. 2.1.6 Trace the pathway of a nervous impulse from the 4th intercostal space to the spinal cord, and from the spinal cord to an intercostal muscle in the same space. 2.1.7 Identify the sympathetic trunk and its connections to an intercostal nerve. 2.1.8 Indicate the origin, location, and termination of the preganglionic and postganglionic sympathetic fibers. 2.1.9 Trace the flow of arterial and venous blood into and out of a typical intercostal space, both anteriorly and posteriorly. 2.1.10 Explain the organization of the arterial and venous structures, including potential collateral pathways, and relate them to the musculature of the thoracic wall. |
SECTRA TABLE WORK: Page 1 of 5
 |
| Tap on image to enlarge |

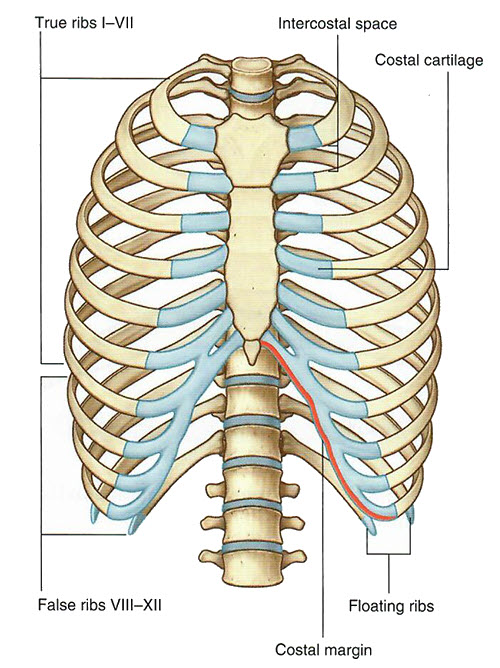
| Add the vertebral column. |
| Add the true ribs (ribs 1-7). These ribs are considered true ribs because each connects to its own costal cartilage, which in turn articulates directly with the sternum. |