
Anterior Abdominal Wall: Lab 4 - Page 5 of 6
| Add the inferior epigastrics and find them on the cadaver. |
| Add the spermatic cord. |
What structures are in the spermatic cord? |
|
|
The structures are the following: 1. The ductus deferens 2. The artery to the ductus deferens 3. The testicular artery and vein 4. The cremasteric artery and vein 5. The genital branch of the genitofermoral nerve (Innervates the cremasteric muscle) 6. Sympathetic and visceral afferent nerve fibers 7. Lymphatics 8. Remnants of the processus vaginalis |
|
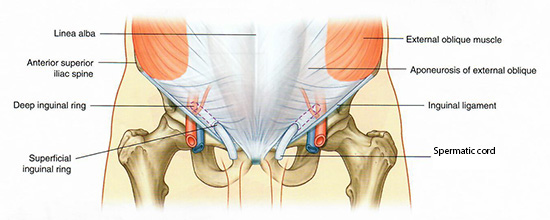
| Highlight the internal abdominal oblique muscle. |
Remember that the extension of the internal abdominal oblique is the cremaster which forms the deep inguinal ring of the inguinal canal.
| Highlight the external abdominal oblique muscle. |
Remember that the extension of the external abdominal oblique is the inguinal ligament which forms the superficial ring of the inguinal canal.
| The inferior epigastric arteries are important landmark. Note that the spermatic cord enters the pelvis via the deep inguinal ring which is just lateral to the inferior epigastric artery. |
Surgeon's love to quiz you about Hesselbach's Triangle. What are the boundaries of the inguinal (Hesselbach's) triangle? |
|
|
Laterally = inferior epigastric artery and vein. |
|
| Demonstrate the boundaries of Hesselbach's Triangle. |