
Neurology Lab 7 - Module 2 - Hearing and Cochlear Mechanism: Page 4 of 4
×
 |
| Tap on image to enlarge |
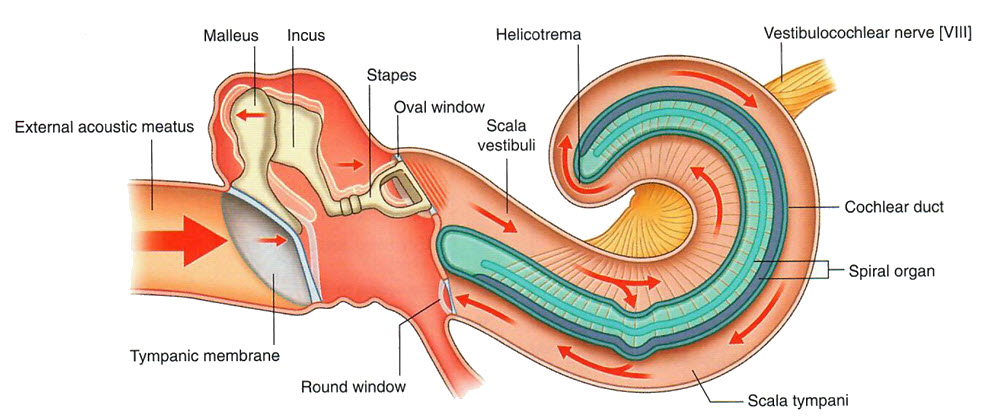
Can you find where the tensor tympani muscle is located? |
|
|
It is the muscle that connects to the malleus at the tympanic membrane in the drawing. |
|
What is the function of the tensor tympani muscle and what nerve innervates this muscle? |
|
|
This muscle is innervated by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V3). This muscle functions to tense the tympanic membrane and decrease the effect of loud noises. |
|
When would these muscles be most useful to you? |
|
|
A rock concert. |
|
There are four cranial nerves that carry pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibers:
- Oculomotor nerve CN III which supplies the ciliary ganglion.
- Facial nerve CN VII which supplies the submandibular ganglion via the chorda tympani and the pterygopalatine ganglion via the greater petrosal nerve.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX which supplies otic ganglion via the tympanic plexus and the lesser petrosal nerve.
- Vagus nerve CN X which supplies pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the foregut and the midgut. Note that the hindgut is supplied by the parasympathetics of the lumbosacral plexus.
Which of these nerves transverse the temporal bone? |
|
|
The chorda tympani, greater petrosal and the lesser petrosal nerves. |
|