Lab 4 - Module 2 - The Hand: Page 9 of 12
Interosseus and Lumbrical Muscles
| Add the Flexor Digitorum Profundus. |
| Add the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis. |
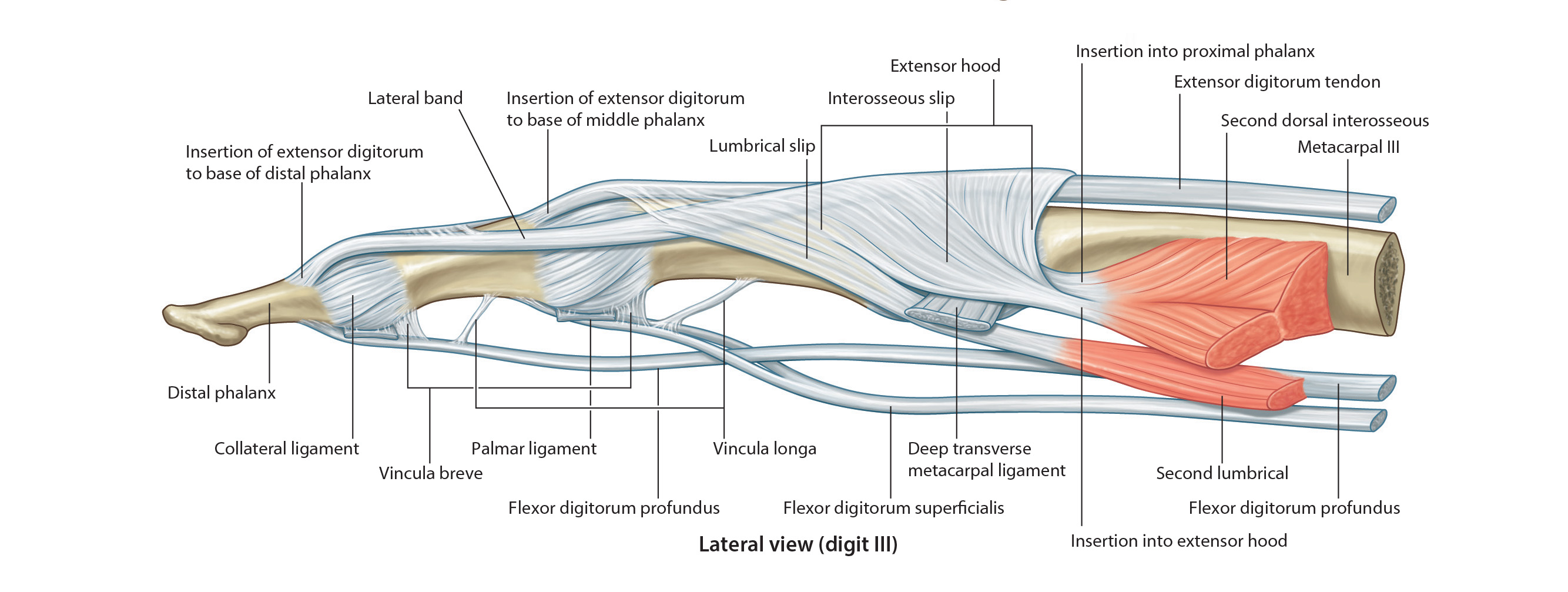
| The tendons of these muscles pass in a common sheath deep to the flexor retinaculum. They then pass deep to the palmar aponeurosis and enter the osseofibrous tunnels digital tunnels. The palmar aponeurosis is the strong, well defined triangular part of the deep fascia covering the soft tissue of the hand. It overlies the long flexor tendons of the palm. The proximal end of the palmar aponeurosis is continuous with the flexor retinaculum. |
| Observe that there are two tendons in each osseofibrous tunnel. In order that these tendons can slide freely over each other during movements of the fingers, each tendon is covered with a synovial membrane. Near the base of the proximal phalanx, the tendon of the flexor digitorum superficialis splits and surrounds the tendon of the flexor digitorum profundus. The halves of the tendon of the flexor digitorum superficialis insert into the margins of the middle phalanx. The tendon of the flexor digitorum profundus, after passing through the split in the tendon of the flexor digitorum superficialis, passes distally to insert into the base of the distal phalanx. |
With this patient, can you explain why the corticosteroids provided relief for a period of time, but the symptoms returned? |
|
|
Think about the waythe tendons slide through this area. |
|