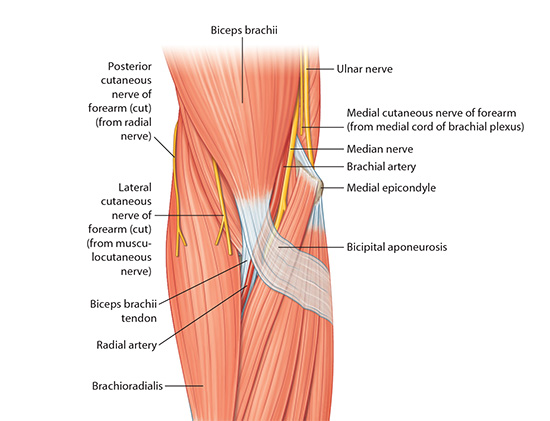
| Triangular space on the anterior surface of the elbow. The cubital fossa is bounded superiorly by an imaginary line connecting the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus, medially by the pronator teres muscle, and laterally by the brachioradialis muscle. The floor of the fossa is formed by the brachialis and supinator muscles. The roof is formed by the deep fascia that is strengthened by the bicipital aponeurosis. The cubital fossa contains the biceps tendon, brachial artery, and its terminal branches (radial and ulnar arteries), and parts of the median and radial nerves. |