
Thorax Lab 3 Module 2
OBJECTIVES:2.3.1 Trace the course of a primary (main), secondary (lobar), and tertiary (segmental) bronchus to at least one bronchopulmonary segment. 2.3.2 Follow the path of pulmonary arteries and veins on the hilar surface of the lung, and trace their distribution to at least one bronchopulmonary segment. 2.3.3 Describe the flow of lymph from each lung, and identify the typical location of associated lymph nodes, whether or not they are visible on the images. 2.3.4 Trace the lymphatic drainage of the thoracic wall, pleura, and lungs, including the sequence of lymph nodes and drainage pathways. |
SECTRA TABLE WORK: Page 1 of 4
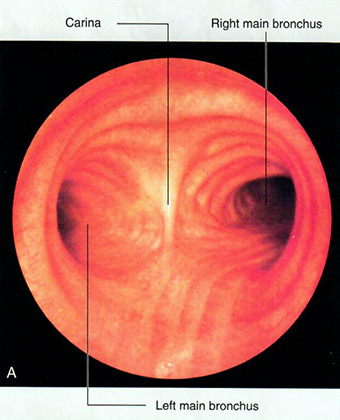
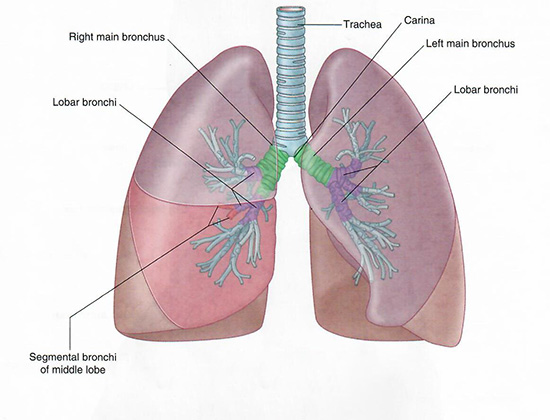
| Begin with the trachea, the main airway conducting air from the larynx to the bronchi. | |
| Add the left and right main (primary) bronchi. |
From this point, the bronchi divide into the lobar (secondary) bronchi, and then into segmental (tertiary) bronchi.
We will examine each lobe and its segmental bronchi individually in the steps that follow.
 |
 |
| Tap on image to enlarge | Tap on image to enlarge |

